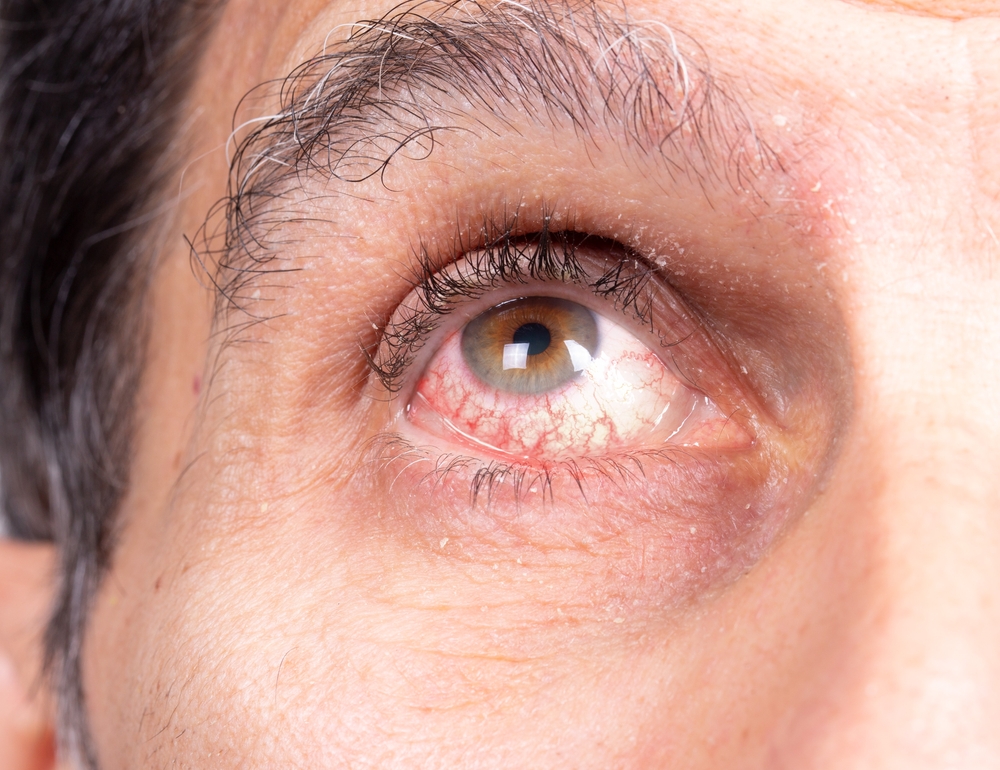
If you have ankylosing spondylitis (AS), you’re likely familiar with chronic back pain and joint stiffness. However, AS doesn’t just affect the spine — it can also impact eye health. Symptoms such as redness, eye pain, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light may not be isolated occurrences but rather indications of uveitis, one of the ocular complications associated with AS.1 If left untreated, uveitis can lead to serious vision impairment.
Monitoring vision changes is just as important as managing back and joint pain. Learn how AS affects eye health and what you can do to protect your vision.
How AS Impacts Eye Health
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine. Research shows that AS can be classified as both an autoimmune disease and autoinflammatory disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues while also triggering excessive inflammation.2
Specifically, innate immune cells play a significant role in the development of ankylosing spondylitis. These immune cells are also highly active in the eyes, contributing to inflammation that can lead to uveitis.3
Because AS is a chronic inflammatory disease, people with AS are at an increased risk of developing recurrent or chronic uveitis compared to those without the condition.4
Common Eye Problems Linked to Ankylosing Spondylitis
Uveitis
By far, the most common eye complication associated with ankylosing spondylitis is uveitis, which affects up to 40% of people with AS.5 Uveitis occurs when the middle layer of the eye becomes inflamed, leading to symptoms such as redness, pain, decreased vision, and sensitivity to light. If left untreated, uveitis can cause vision loss or complications like glaucoma and cataracts.6
Dry Eye Syndrome
People with ankylosing spondylitis are also at a higher risk of developing dry eye syndrome, a condition where the eyes do not produce enough tears to stay lubricated. This can result in irritation, a gritty feeling in the eyes, and even damage to the cornea over time.7
Types of Uveitis
Uveitis can affect different parts of the eye. The type of uveitis someone develops often depends on the underlying cause, including whether it is linked to AS.
Acute Anterior Uveitis (Iritis)
This is the most common type of uveitis. It affects the front part of the eye (the iris) and is often acute, meaning it develops suddenly. Anterior uveitis is characterized by eye redness, pain, and light sensitivity, and it typically occurs in one eye at a time. If treated early, anterior uveitis usually resolves without permanent damage.5,8
Intermediate and Posterior Uveitis
Less common is intermediate or posterior uveitis, which affects the middle and back portions of the eye. These forms of uveitis can cause blurred vision, floaters, and retinal complications. They tend to be more difficult to treat and may require long-term management.8
Symptoms of Uveitis in AS
Because AS-related uveitis often develops suddenly, it’s important to recognize the symptoms early and seek medical attention. Symptoms typically appear in one eye but can alternate between eyes over time.
Common signs of uveitis include:
- Eye pain: A deep, aching pain in or around the eye.
- Redness: Inflammation causes visible redness in the affected eye.
- Sensitivity to light: Bright light may cause discomfort or worsen symptoms.
- Blurred vision: Inflammation can interfere with clear vision.
- Excessive tearing: The eye may produce more tears in response to irritation.
- Floaters: Dark spots or specks may appear in the visual field.
If you experience any of these symptoms, don’t brush them off! Early treatment is key to preventing complications.
Who Diagnoses Uveitis?
When eye symptoms arise, knowing who to see can make all the difference. While a rheumatologist manages ankylosing spondylitis (AS), they are not eye specialists. An ophthalmologist, a medical doctor specializing in eye diseases, is more equipped to diagnose and treat uveitis.8
It’s still important to inform your rheumatologist if you develop uveitis so they can adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Treatment Options for Uveitis
Treating uveitis requires addressing both eye inflammation and the underlying systemic disease. The goal is to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent recurrences.
- Eye Drops: Commonly used for anterior uveitis, anti-inflammatory eye drops are the first line of defense.9
- Pills: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be used in milder cases to reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups, not just for uveitis but also for ankylosing spondylitis. For more extensive inflammation or when eye drops are insufficient, oral steroids may be prescribed.9
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases where rapid or targeted treatment is necessary, steroids can be injected directly into or around the eye.8,9
If steroids alone do not adequately control the inflammation, long-term therapy may be an option. This can include immunosuppressive drugs or biologic medications, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, to modulate the immune system’s response and reduce inflammation.8
The specific treatment plan will depend on the type of uveitis, its underlying cause, and the individual’s response to therapy. Regular follow-up with an eye care professional is crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary.
Can You Prevent Uveitis in AS?
While there’s no foolproof way to prevent uveitis, managing AS effectively can reduce the risk of flare-ups. Here are some key steps:
- Follow your AS treatment plan: Taking prescribed medications, especially biologics, can lower inflammation and reduce the risk of uveitis.10
- See an eye doctor regularly: Routine eye exams can catch early signs of inflammation before symptoms worsen.8
- Watch for early warning signs: Seeking treatment at the first sign of eye discomfort can prevent complications.8
Schedule a Consultation Today
If you’re experiencing eye discomfort or are concerned about the effects of ankylosing spondylitis on your vision, don’t wait — early intervention is key! At IDYLLIC Infusion Treatment Center, we work hand-in-hand with ARBDA doctors, who specialize in managing autoimmune conditions like AS and their complications. We offer cutting-edge infusion therapies designed to reduce inflammation and improve overall well-being.
Protecting your vision is just as important as caring for your joints and spine. Let’s work together to keep your eyes healthy! Schedule a consultation today and take the first step toward better health.
1https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1521694216300808?via%3Dihub
2https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-021-00625-y
3https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4186974/
4https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4956824/
5https://nass.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Uveitis-factsheet-2015.pdf
6https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uveitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378734
7https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10607705/
8https://health.clevelandclinic.org/eye-pain-ankylosing-spondylitis
9https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/uveitis